A Low Blood pressure value of less than 90 mm Hg for the top number (systolic) or 60 mm Hg for the bottom number (diastolic) is called low blood pressure.
What one individual considers low blood pressure may be considered normal by another. Low blood pressure can cause dizziness and fainting, or it can cause no symptoms at all. Low blood pressure can be life-threatening at times.

Low blood pressure can be caused by anything from dehydration to significant medical issues. It’s critical to determine the cause of low blood pressure so that it can be addressed if necessary.
Variants of Low Blood Pressure
Postural Hypotension:
This is a fall in blood pressure that occurs when you get up from a seated or lying down position. Dehydration, long-term bed rest, pregnancy, certain medical disorders, and some drugs are among the causes. In elders, this sort of low blood pressure is common.
After food hypotension (Postprandial)
This drop in blood pressure occurs 1 to 2 hours after eating. It primarily affects elderly persons, particularly those with high blood pressure or conditions like Parkinson’s disease. Small, low-carbohydrate meals, increased water consumption, and avoidance of alcohol may assist in relieving symptoms.
Neurally mediated hypotension:
This is a fall in blood pressure that occurs after a prolonged period of standing. Young adults and children are the most commonly affected by this sort of low blood pressure. It could be caused by a loss of communication between the heart and the brain.
Symptoms
Low blood pressure (hypotension) symptoms may include:
- Blurred or fading vision
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Fainting
- Fatigue
- Trouble concentrating
- Nausea

Low blood pressure can be a sign of an underlying health problem in some people, especially if it lowers quickly or is accompanied by symptoms.
When Low Blood Pressure is Serious
A drop in blood pressure that occurs suddenly might be harmful. Dizziness and fainting can occur when blood pressure drops by 20 mm Hg — for example, from 110 mm Hg systolic to 90 mm Hg systolic. Large drops, such as those accompanied by uncontrollable bleeding, serious infections, or allergic reactions, can be fatal.
Shock is a condition caused by extremely low blood pressure.
Symptoms of shock:
- Confusion, especially in older people
- Cold, clammy skin
- Decrease in skin coloration
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Weak and rapid pulse
Seek emergency medical treatment if you develop signs of severe low blood pressure (hypotension) or shock.
Blood pressure is only considered dangerously low if it produces symptoms, according to most doctors. Minor dizziness or light headedness can be induced by a variety of factors, including excessive exposure to the sun or usage of a hot tub. To acquire a proper diagnosis, you should see a medical professional.
If your blood pressure is regularly low but you are otherwise healthy, your provider may just monitor you during normal health visits.
Causes
A healthy blood pressure reading is less than 120/80 mm Hg. Body position, breathing, food and drink, medications, physical condition, stress, and time of day all influence blood pressure throughout the day.
Pregnancy: Blood vessels expand rapidly during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. Blood pressure may decline as a result of the alterations. During the first 24 weeks of pregnancy, low blood pressure is frequent. After delivering birth, blood pressure normally returns to pre-pregnancy levels.

Heart and heart valve Diseases: Low blood pressure can be caused by a heart attack, heart failure, heart valve dysfunction, or a very low heart rate.
Hormone-related diseases: Blood pressure may decline as a result of conditions affecting the parathyroid or adrenal glands. Blood pressure can be lowered by low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) and, in some cases, diabetes.
Dehydration: The amount of blood in the body (blood volume) reduces when the body is dehydrated. Blood pressure may decline as a result of this. Dehydration can be caused by fever, vomiting, severe diarrhoea, abuse of diuretics, and vigorous activity.
Severe infection: When an infection in the body reaches the bloodstream, it can cause septic shock, which is a life-threatening reduction in blood pressure.
Severe allergic reaction: A quick and dramatic drop in blood pressure is one of the symptoms of a severe allergic reaction.
Nutrient deficiency in the diet: Vitamin B-12, folate, and iron deficiency can prevent the body from generating enough red blood cells, resulting in low blood pressure.
Risk factors
Low blood pressure can affect everyone.
Age: Adults over the age of 65 are more likely to have drops in blood pressure after standing or eating. Children and young adults are most affected by neurally mediated hypotension.
Medications: Low blood pressure is increased by several medications, particularly various blood pressure medications.
Diagnosis
Blood tests can diagnose low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), high blood sugar (hyperglycaemia or diabetes) or a low red blood cell count (anaemia), all of which can lower blood pressure.
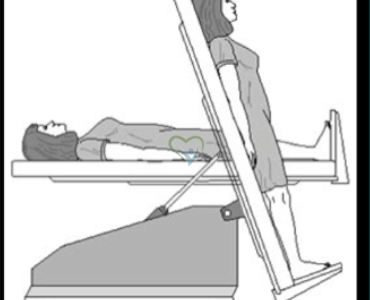
Tilt table test can evaluate how the body reacts to changes in position.
Electrocardiogram identify the conditions that can cause low BP like low heart rate, High heart rate
Treatment
Low blood pressure that is symptomless or has only minor symptoms is rarely treated.
The treatment for low blood pressure symptoms is determined by the cause. If a drug causes low blood pressure, for example, your doctor may suggest changing or stopping the medicine or lowering the dose. If you want to change or stop taking your prescription, talk to your doctor first.
If the cause of low blood pressure is unknown or no treatment exists, the goal is to raise blood pressure and relieve symptoms. There are numerous options depending on your age, health, and type of low blood pressure:
Use more salt: Experts normally advise minimising salt (sodium) because it can significantly raise blood pressure. However, for persons with low blood pressure, this can be beneficial. Nevertheless, too much sodium can cause heart failure, especially in the elderly. As a result, it’s critical to consult with a doctor before increasing your salt intake.
Drink more water: Fluids help to increase blood volume and avoid dehydration, which are both crucial in the treatment of hypotension.
Compression stockings: They improve blood flow from the legs to the heart

Home remedies and a healthy lifestyle
Consume more water, less alcohol
Even when consumed in moderation, alcohol dehydrates the body and lowers blood pressure. Water prevents dehydration by increasing the volume of blood in the body.
Body positions
From a supine or sitting position, slowly rise to a standing position. Don’t sit with legs crossed.
If you’re experiencing low blood pressure feelings when standing, cross your thighs like scissors and squeeze. Alternatively, place one foot on a table or chair and lean forward as far as possible. These exercises help to increase blood flow from the legs to the heart.
low-carb meals
Eat small meals several times a day to help prevent blood pressure from lowering significantly after meals. High-carbohydrate foods including potatoes, rice, pasta, and bread should be avoided.
Exercise regularly
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity every day as a general objective. Exercising in hot, humid weather is not recommended.
Diet For Low Blood Pressure
Drink coffee with your meals — Ensure that you have a cup of coffee with your meal. Coffee, as well as any other caffeinated beverage, can raise blood pressure. If you have low blood pressure, a cup of coffee in the morning can help you feel better right away. It’s also a good addition to your meals if you’re suffering from orthostatic hypotension.
Eat complex carbohydrates at every meal — A low-carbohydrate diet can cause your blood pressure to rise. If you’re going to add carbs to your diet, go for complex carbs like oatmeal, whole wheat bread, and barley rather than macaroni and white bread.

Almonds and raisins as a snack — Almonds and raisins are the simplest way to manage low blood pressure at home. Raisins are excellent Ayurvedic therapy for naturally treating hypotension. soak raisins in water overnight and eat them on an empty stomach in the morning, along with the water they were soaked in. You can experiment with these for a few weeks or months. Another possible home cure for low blood pressure is almond. You can do the same thing with almonds as you did with raisins.
Carrot and Beetroot juice – A glass of fresh carrot juice with honey first thing in the morning can help control blood pressure by regulating heart and kidney functions. Beetroot juice, once again, is a powerful antidote for blood pressure control. Consuming two glasses of beetroot juice every week for week can help patients with hypotension.
Drink lots of water: Aim for 2 to 3 litres of water every day. In addition, include beverages such as coconut water in your low blood pressure diet.
Basil Leaves: Chewing basil leaves in early morning helps to fight against Low Blood pressure. Basil leaves contain Potassium magnesium and vitamin C which may help’s in maintaining your blood pressure
Green Tea: Green tea is high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making it an excellent choice for treating low blood pressure.

Licorice Root: The root powder, when infused with warm water and consumed on a regular basis, can help persons with hypotension because of its anti-inflammatory and adaptogenic qualities.

