Anxiety cause cardiac arrest, physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, chest pain, and shortness of breath, which may mimic the symptoms of a heart attack. However, anxiety itself is not typically the direct cause of a cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is caused by a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, which leads to the heart stopping or beating irregularly. This can happen as a result of heart disease or other underlying medical conditions. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of a heart attack or cardiac arrest.
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a normal and often healthy emotion. However, when a person regularly feels disproportionate levels of anxiety, it might become a medical disorder. Anxiety is a feeling of unease, such as worry or fear, that can be mild or severe. Anxiety disorders form a category of mental health diagnoses and are the most common mental illness in the United States. Anxiety disorders are real, serious medical conditions—just as real and serious as physical disorders such as heart disease or diabetes.

Anxiety disorders are characterised by a variety of symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
- Persistent worrying or obsessing about everyday problems
- Fear or avoidance of certain situations
- Physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and feeling tense or jumpy
- Difficulty sleeping or concentrating
There are several different types of anxiety disorders, including generalised anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Each type of anxiety disorder has its own unique set of symptoms and characteristics.
Anxiety disorders are treatable, and many people with these conditions can lead fulfilling lives. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. If you think you may have an anxiety disorder, it is important to seek professional help.
Anxiety in the population
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects people of all ages, genders, and cultures. However, the prevalence of anxiety can vary across different populations.
In general, anxiety disorders are more common in women than in men. According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), around 25.1% of children between the ages of 13 and 18 have an anxiety disorder. This number increases in young adults, with around 30% of adults aged 18–29 being affected by an anxiety disorder.
Anxiety disorders also tend to be more common in certain ethnic and racial groups. For example, research has shown that anxiety disorders are more common in African American and Hispanic populations than in non-Hispanic whites.
Anxiety disorders are also more common in people with lower income and education levels. People who live in poverty or who have less education may be at a higher risk of developing anxiety disorders.
It’s important to note that these are just some examples of the population groups that may be more likely to experience anxiety, and there may be other population groups that are not listed here. Additionally, the prevalence of anxiety can vary depending on the context and cultural factors.
It’s important to seek professional help if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety that are impacting your daily life. A healthcare professional can help you find the best treatment for you, regardless of your population group.
Common causes of anxiety?
There are several common causes of anxiety, including:
- Genetics: Anxiety can run in families, and certain genetic predispositions may make a person more susceptible to developing anxiety disorders.
- Trauma or life events: Traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or the loss of a loved one, can contribute to the development of anxiety.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, have been linked to anxiety disorders.
- Chronic medical conditions: Long-term health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes, can also contribute to the development of anxiety.
- Substance abuse: Using drugs or alcohol can trigger symptoms of anxiety or make existing anxiety worse.
- Stress: Chronic stress, whether from work, school, or personal relationships, can also contribute to the development of anxiety.
It’s also worth noting that anxiety can be a symptom of other underlying medical or mental health conditions. So it is important to see a healthcare professional if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety to get a proper diagnosis and treatment.
How anxiety is related to heart disease
Anxiety and heart disease have been found to have a complex relationship. Anxiety can cause physical symptoms such as a rapid heartbeat, chest pain, and shortness of breath, which may mimic the symptoms of a heart attack.
Chronic stress and anxiety can also lead to the development of other risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.
Additionally, people with heart disease are at an increased risk of developing anxiety and depression, which is commonly referred to as “cardiac anxiety.” This is a type of anxiety that results from the fear of having another cardiac event.
Studies have shown that people with both heart disease and anxiety have a higher risk of dying or experiencing another cardiac event. Therefore, it is important for individuals with heart disease to have their anxiety treated along with their heart disease.
Managing stress through exercise, therapy, or medication can help reduce the risk of developing heart disease and also improve heart health outcomes in those who already have heart disease.
Common age group affected by anxiety
Anxiety can affect people of all ages, but it typically develops in adolescence or early adulthood. Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions in children and adolescents.
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), around 25.1% of children between the ages of 13 and 18 have an anxiety disorder. This figure rises among young adults, with approximately 30% of adults aged 18–29 suffering from an anxiety disorder.
It’s also important to know that older adults can also have anxiety disorders, and the number of people who have them goes up as they get older.
While anxiety can occur at any age, it is important to seek professional help if you or your loved one is experiencing symptoms of anxiety. Early intervention can greatly improve the chances of recovery and prevent the condition from worsening.
Common types of anxiety
There are several common types of anxiety disorders, including:
- Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD): is characterised by excessive, unrealistic worry and tension, even if there is little or nothing to provoke the anxiety.
- Panic disorder: is characterised by recurrent, unexpected panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, and feelings of impending doom.
- Social anxiety disorder (SAD): characterised by a strong and persistent fear of social or performance situations and intense feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, or being judged.
- Specific phobias: characterised by a persistent and excessive fear of a specific object or situation, such as heights, flying, or enclosed spaces.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): characterised by persistent, uncontrollable thoughts and repetitive behaviours that a person feels driven to perform in response to those thoughts.
- Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): is characterised by a persistent and overwhelming emotional response to a traumatic event, such as military combat, sexual or physical assault, or an accident.
It is important to note that these are just some examples of the most common types of anxiety disorders, and there may be other types of anxiety that are not listed here. It’s important to see a healthcare professional if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety to get a proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest is a sudden and unexpected loss of heart function, breathing, and consciousness. It occurs when the heart’s electrical system malfunctions, causing the heart to stop beating or to beat irregularly. This can happen as a result of various underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, but also due to external factors like trauma, electric shock, or drug overdose.
During a cardiac arrest, blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs, and death can occur within minutes if the person does not receive immediate medical attention. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the use of a defibrillator are usually the first lines of treatment for someone experiencing cardiac arrest.
It’s important to note that cardiac arrest is different from a heart attack, which is caused by a blockage in the blood flow to the heart. While a heart attack can lead to cardiac arrest, not all cardiac arrests are caused by heart attacks.
Risk factors for cardiac arrest due to anxiety
Anxiety can be a risk factor for cardiac arrest; however, it is typically not the direct cause of a cardiac arrest. However, chronic stress and anxiety can lead to the development of other risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. The following are some of the risk factors associated with cardiac arrest that can be related to anxiety:

- High blood pressure: chronic stress and anxiety can lead to an increase in blood pressure, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Heart rate variability: Anxiety can cause changes in the heart rate variability, which can cause the heart to beat irregularly, increasing the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Atherosclerosis: Studies have shown that chronic stress and anxiety can lead to the development of plaques in the arteries, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Inflammation: Chronic stress and anxiety can lead to an increase in inflammation throughout the body, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
- Substance abuse: People who abuse drugs or alcohol are at increased risk of cardiac arrest.
- Smoking: People who smoke are at an increased risk of cardiac arrest.
It is important to note that these are just some examples of the risk factors associated with cardiac arrest, and there may be other risk factors that are not listed here. It’s important to see a healthcare professional if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety to get a proper diagnosis and treatment.
How to stay away from anxiety
There are several things you can do to reduce your risk of developing anxiety or to manage the symptoms of anxiety if you already have an anxiety disorder. Here are a few strategies that may be helpful:
- Regular exercise has been shown to reduce anxiety symptoms, boost mood, and improve overall health.
- Practice relaxation techniques: deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga are all examples of relaxation techniques that can help reduce symptoms of anxiety.
- Get enough sleep: Lack of sleep can worsen symptoms of anxiety, so it’s important to get enough rest each night.
- Eat a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall physical and mental well-being.
- Don’t drink alcohol or use drugs. Both can make anxiety symptoms worse and can lead to addiction.
- Talk to a therapist or counselor. A therapist or counsellor can help you work through the underlying issues that may be contributing to your anxiety and can teach you coping strategies to manage symptoms.
- Medications: Medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed to help reduce symptoms of anxiety.
It is important to note that different strategies may work better for different people, and it’s important to find what works best for you. It is also important to seek professional help if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety that are impacting your daily life. A healthcare professional can help you find the best treatment for you.
How yoga helps to reduce anxiety
Yoga is a form of exercise that combines physical poses, controlled breathing, and meditation or relaxation. Research has shown that yoga can be an effective tool for reducing symptoms of anxiety. Here are a few ways in which yoga may help reduce anxiety:
- Reducing stress: Yoga practises such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress and tension in the body, which can decrease symptoms of anxiety.
- Improving mood: Yoga has been shown to increase levels of the feel-good hormone serotonin, which can improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety.
- Changing the way you think: Yoga can help change the way you think and respond to anxiety-provoking situations by teaching you to focus on the present moment rather than worry about the future or dwell on the past.
- Improving overall well-being: Yoga is a mind-body practise that can help to improve overall physical and mental well-being. It can also help to improve sleep, which can be an important factor in managing anxiety.
- Mindfulness: Yoga helps to improve mindfulness, which is the ability to pay attention to the present moment. This helps reduce anxiety by making you aware of your thoughts and feelings and allowing you to respond to them in a more constructive way.
It is important to note that yoga should be used in addition to, not as a replacement for, other treatments for anxiety disorders. Before starting a new exercise programme, it’s important to talk to a doctor or nurse, especially if you have a medical condition.
A few yoga poses to combat anxiety
There are several yoga poses and practises that can be particularly helpful for reducing symptoms of anxiety. Here are a few examples:
- Child’s Pose: This pose helps to calm the mind and reduce tension in the shoulders and back.
- Downward-facing dog: This pose helps to release tension in the neck, shoulders, and back and can also help to improve mood.
- Standing forward bend: This pose helps to release tension in the back and neck and can also help to calm the mind.
- Warrior 2: This pose helps to build confidence and can help reduce feelings of anxiety and stress.
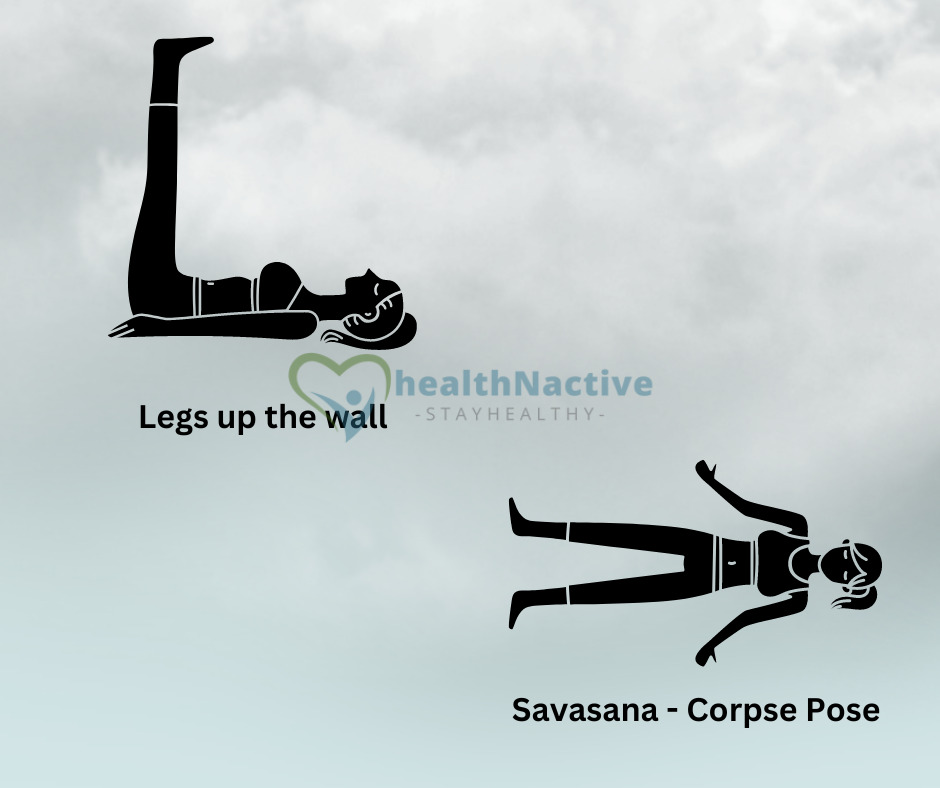
- Legs up the wall: This pose helps to reduce tension in the legs and lower back and can also help to calm the mind.
- Savasana (Corpse Pose): This pose is often used at the end of yoga practise, and it can help to reduce stress, tension, and anxiety.
- Pranayama (breathing techniques): Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing, Nadi Shodhana (alternate nostril breathing), and Ujjayi (victory breath) can help reduce anxiety by calming the nervous system.



It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of yoga poses and practises that can be helpful for reducing symptoms of anxiety. To find a yoga practise that fits your needs and skill level, you should talk to a qualified yoga instructor.
Yoga precautions for heart patients
Yoga can be beneficial for heart patients, but it’s important to take certain precautions to ensure that the practise is safe and effective. Here are a few things to keep in mind if you have heart disease and are considering practising yoga:
- Consult with your doctor: It’s important to consult with your doctor before starting any new exercise programme, especially if you have heart disease. Your doctor can help you figure out if yoga is a good way to work out for you and can point out any poses or sequences that may be especially helpful or dangerous.
- Start slowly: If you haven’t exercised in a while, it’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your practise.
- Avoid poses that put pressure on the chest: Certain yoga poses, such as backbends, can put pressure on the chest and increase the risk of angina (chest pain) or other cardiac symptoms. It’s important to avoid these poses or modify them so that they are safe for your condition.
- Watch for warning signs: During yoga practise, it’s important to be aware of warning signs of cardiac distress, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness. If you have any of these symptoms, you should stop practising right away and see a doctor.
- Avoid fast breathing practises: Pranayama, or breathing practises that involve fast breathing, or holding your breath, should be avoided if you have heart disease.
- Be aware of your limits. It’s important to listen to your body and be aware of your limits during yoga practise. If you feel fatigued or experience any discomfort, stop your practise and rest.
It’s important to work with a qualified yoga teacher who has experience working with people with heart disease and can help you modify your practise to make it safe and effective.
What foods can help reduce anxiety?
There is no specific diet that is guaranteed to reduce symptoms of anxiety, but research suggests that certain foods and nutrients may be beneficial in managing anxiety. Here are a few examples:

- Omega-3 fatty acids: Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), flaxseeds, and chia seeds, may help to reduce inflammation and improve mood.
- Complex carbohydrates: Eating complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, can help to stabilise blood sugar levels, which can help to reduce feelings of anxiety.
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is needed for the production of neurotransmitters, including serotonin and GABA, which are important for regulating mood. Foods high in vitamin B6 include chicken, fish, and potatoes.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that helps regulate the nervous system. Foods high in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts and seeds, and avocado.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that live in the gut and can help to improve gut health and mental well-being. Foods high in probiotics include yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi.
It’s worth mentioning that it’s important to have a well-balanced diet; eating a variety of foods can provide the body with the necessary nutrients to function well. Also, it is important to seek professional help if you are experiencing symptoms of anxiety that are impacting your daily life. A healthcare professional can help you find the best treatment for you.

