Atrial Fibrillation Treatment must begin as soon as possible. Your treatment approach for AF may take into account a variety of factors, such as: the nature or cause of the arrhythmia; the symptoms; medications; age; the history of one’s own and one’s family’s health Additional health issues Medications
Treatment options include
Medications
Cardioversion
Catheter ablation
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment Medications
The majority of AF patients initially receive pharmaceutical recommendations to normalize their cardiac rhythm, treat AF symptoms, or reduce their risk of stroke. Medications may include:
Rate Control
- In order to normalise their heart rate, manage AF symptoms, or lower their risk of stroke, the majority of AF patients initially obtain pharmaceutical recommendations.
- Beta blockers reduce heart rate, relax blood vessels, and facilitate the heart’s ability to pump blood.
Rhythm Control
- Drugs that block sodium channels reduce the electrical conductivity of the heart and help with rhythm issues.
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs help to preserve or restore normal sinus rhythm.
Blood Thinners
- Blood clot and risk of stroke is decreased with anticoagulant treatment.

Cardioversion
A regulated, low-dose shock to the heart is used in cardioversion to change aberrant rhythms to sinus rhythms. In a hospital setting like the emergency room, intensive care unit, recovery room, special procedure room, or electrophysiology lab, it is often carried out under sedation. A cardioversion frequently results in the recurrence of AF.
Catheter Ablation
When medicine is ineffective, catheter ablation is the recommended course of treatment for patients. Catheter ablation is a technique to restore the improper electrical impulses that the heart sends out and result in an irregular cardiac rhythm.
The majority of patients who have catheter ablation therapy see a long-term decrease in the frequency of arrhythmia episodes, a symptomatic improvement, and an increase in quality of life.
What is catheter ablation?
Catheter ablation is a technique to address the improper electrical impulses that the heart sends out and result in an irregular cardiac rhythm.
How is the procedure performed?
- An electrophysiologist, an expert in heart rhythm, performs a catheter ablation treatment.
- A tiny incision is made in the patient’s leg during the treatment, and a thin tube called a catheter is inserted. It is then threaded up into the leg artery and into the heart. An electrophysiologist utilises a catheter to create a tiny scar in a particular area of the heart tissue with the help of 3-D imaging technology. Cryoablation or radio-frequency ablation are both used to perform the operation.
Catheter ablation benefits

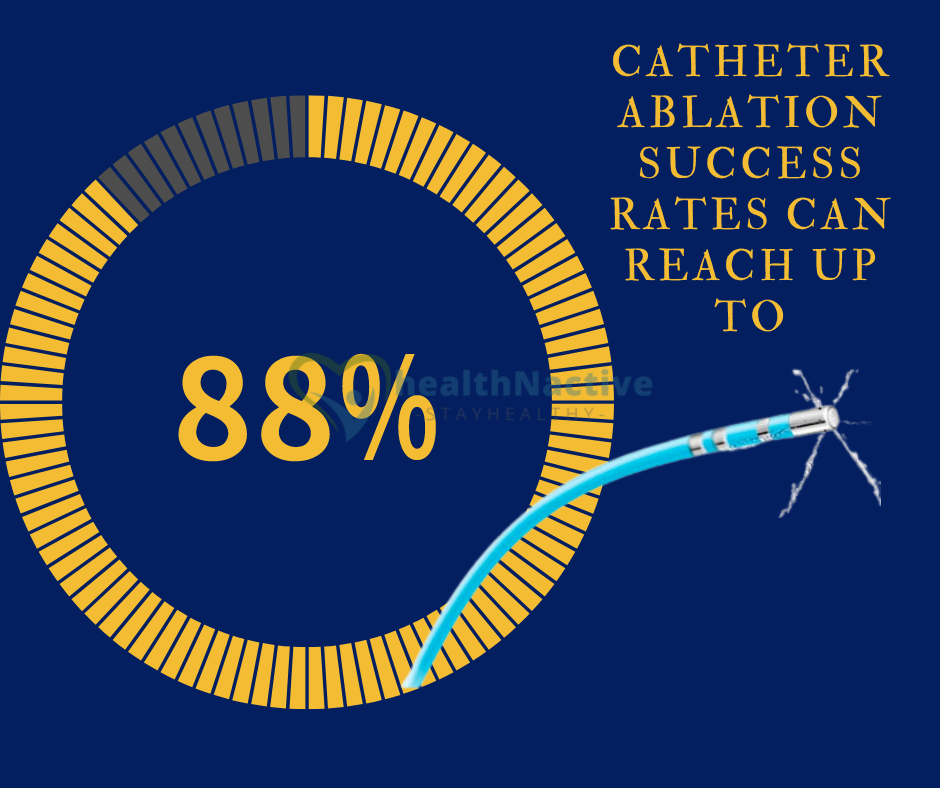
Success Percentage of catheter ablation
The outcome of a catheter ablation surgery may be predicted by a wide range of variables. These include age, hypertension, sleep apnea, obesity, and increasing left atrial size. Before your operation, discuss these issues with your doctor.
Success rates for catheter ablation are up to 88%.
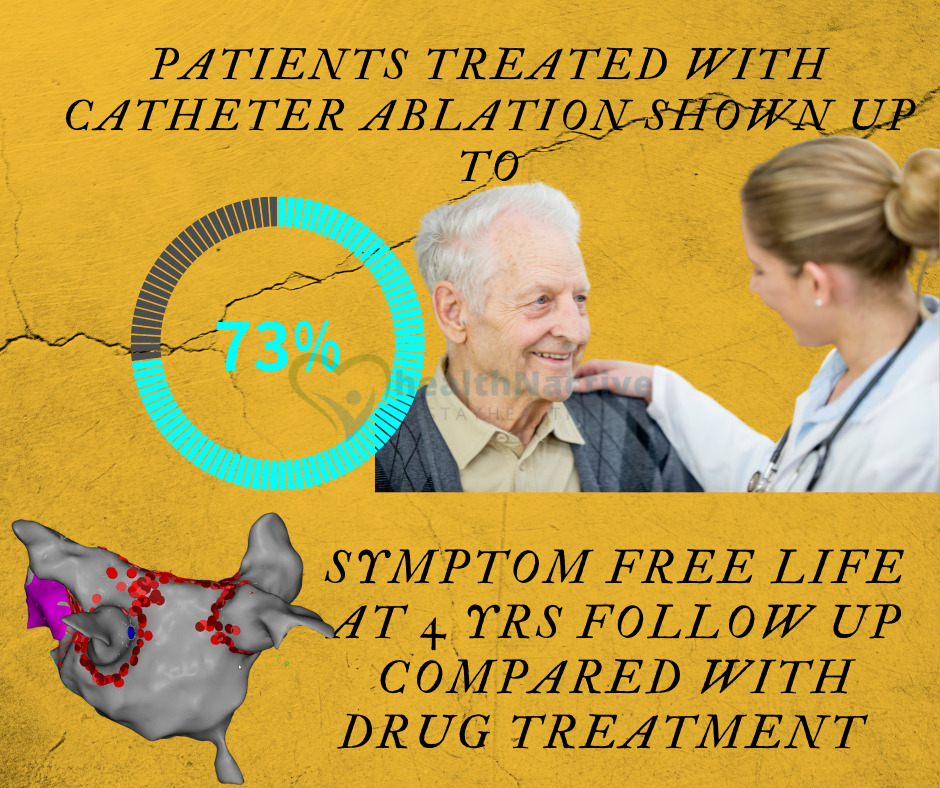
Improvement in quality of life with catheter ablation
The recent research indicates that catheter ablation of AF considerably improves quality of life more than medication therapy, indicating that treating AF can restore quality of life.
Suggested reading: Atrial Fibrillation Awareness Guide

